All Posts / Implementing the Essential Eight Framework: Strengthening Your Organization’s Cybersecurity Defenses.
Cyber security
Implementing the Essential Eight Framework: Strengthening Your Organization’s Cybersecurity Defenses.

One of the major issues that we are now facing as a society is cybercrime. Its effects on the general population and organizations increase by the day. In the past ten years, the cybersecurity sector has seen a significant transformation and is still quickly developing. An organization’s reputation, finances, and even national security could all suffer from a cyberattack. Because of this, cyber security has become a top issue for all types of businesses worldwide.
Following these developments, the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) developed the Essential Eight Framework, to strengthen our cyber resilience and cyber defenses. This has been the ultimate solution that will bridge the gap between cybersecurity giants and the small enterprises that are just coming up.
The Essential Eight Framework: What is it and How Does it Serve You?
Due to the cyber security surge across the globe, The Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) created the Essential 8 list of eight high-priority activities to assist Australian businesses in lowering their cyber security risks. These eight guidelines, according to ASD, can stop up to 85% of cyberattacks on their own. They can be modified to meet the unique requirements of various businesses because they are created to be adaptable and scalable. They offer a generally positive ROI and serve as a solid starting point for assessing a cyber security strategy.
The Birth of the Essential 8
How did the Essential 8 Framework come into being?
- Phase 1:
In its initial stages in 2014, the Australian Government departments and agencies made the first four guidelines mandatory.
- Phase 2:Later on, in 2017, the first official publication was released. After this, the PSPF (Protective Security Policy Framework) of the Attorney-General’s Department mandated the other four.
- Phase 3:In addition, the Australian Government Information Security Manual (ISM), which was released by ASD in December 2019, recommended that Australian firms should apply the eight crucial mitigation methods as a minimum. Even if the introduction of this framework was in phases, each of the phases served a significant role in improving the defense against cyber goons. With this framework, it is far more difficult for cybercriminals to infiltrate an organization’s information security system.
How exactly does Essential 8 Benefit your Business?
If you are like me, you are probably asking, “ What’s in it for me?” If you are looking for the answer to this question, then read on! I have broken it down for you bit by bit!
The Essential 8 framework is made to help reach their business objectives all over the world by offering a series of doable actions that can be implemented to strengthen their cyber security posture. Below is a list (not exhaustive) of the advantages that you are set to enjoy, after implementing the framework:
-
- Protection against cyberattacksOrganizations like yours need to be ready to protect against cyberattacks, which are getting more frequent and sophisticated. By implementing the Essential 8 framework, your organization greatly lowers the risk of cyberattacks and lessens the potential effect of those assaults.
- Customized protection
The framework offers a prioritized set of controls that businesses can install based on the level of risk to the organization, which is one of its main advantages. Instead of attempting to deploy a broad set of controls that might not be essential or effective, this will aid your firm in concentrating your resources and improving your cybersecurity posture. This is good news, right?
-
- Flexibility
The Essential Eight’s lack of prescriptiveness is another advantage. You are always free to select how to put the strategies into practice based on your unique requirements and situation.
-
- Compliance with cyber security laws
These regulations enable you to comply with numerous cyber security laws and requirements without breaking a sweat. Whether you are in the finance sector or the health sector, or whichever sector you are in, Essential 8 helps prove compliance with these rules and requirements that are set for businesses.
-
- Better Branding and Positioning
Organizations can also benefit from protecting their reputation and brand image by using these stipulated frameworks. Cyberattacks can seriously harm an organization’s reputation, especially if private information or intellectual property is compromised.
Your organization can show stakeholders, partners, and clients that they take cyber security seriously and are taking proactive measures to safeguard their assets and data by putting the Essential 8 mitigation methods into practice.
Maturity Levels of the Essential 8
For each risk reduction strategy, four unique developmental stages have been defined to aid organizations in evaluating the progress of their implementation of these security solutions. The basic 8 is split into two groups:
-
- The first four frameworks(which were first introduced in 2014):
They are referred to as the “essential baseline” and are advised for all organizations.
-
- The final four(introduced in 2017):
They are referred to as “advanced” and are advised for businesses with established cybersecurity practices.
As I like to tell myself, there is always room for improvement! Similarly, an organization can advance through each of the four maturity levels for a strategy to strengthen its security posture. From “Ad Hoc” to “Optimized,” the maturity levels range, with each level building on the one before it. Here’s a summary of the maturity levels:
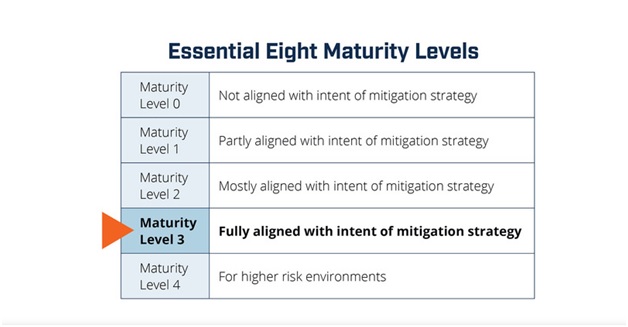
The four Maturity Levels include:
-
- Maturity Level 0:
This is the starting playground of most organizations. At this level, there is no formal plan or method in place to administer cyber security controls; they are instead deployed on an as-needed basis. This level is also called the Ad-hoc level.
-
- Maturity Level 1:
This level is also known as the Emerging level. At this stage, firms start to formalize their plans and procedures for putting cyber security measures in place. Although there is a higher level of awareness and comprehension of the risks and hazards, controls are still implemented in a reactive manner.
-
- Maturity Level 2:
This is famously known as the Established Level. This is where the organization’s comprehensive risk management system incorporates cyber security procedures. The organization has a structured plan and method for managing cyber security, and controls are implemented proactively. At this stage, there is no taking chances, the frameworks must be implemented round the clock!
-
- Maturity Level 3:
Also known as the Dynamic level, this is the highest level of maturity that there is. The firm has a sophisticated and thorough cyber security procedure in place at this point, which is often evaluated and updated to handle emerging threats and hazards. There is a strong culture of cyber security awareness throughout the company, and it is proactive in finding and resolving cyber security risks. The organization’s cyber security controls must be regularly monitored and reviewed as part of a continuous improvement process.
How to Implement the Essential Eight Strategies
The cyber maturity model uses a whole-of-organizational approach to assist firms in developing their cyber capacity. It draws attention to the threats to various departments and functions within an organization from cyberattacks and cyber defense. It guarantees the organization-wide alignment of cyber security strategies, cyber procedures, and cyber awareness.
In the following sections, the strategies and maturity levels of the Essential Eight framework will all be thoroughly covered, following the recommendations given by the 2023 ACSC annual cyber threat report. The significance of the Essential Eight in cybersecurity and how it may help enterprises will not be left out. Now let’s explore the Eight strategies of the framework:
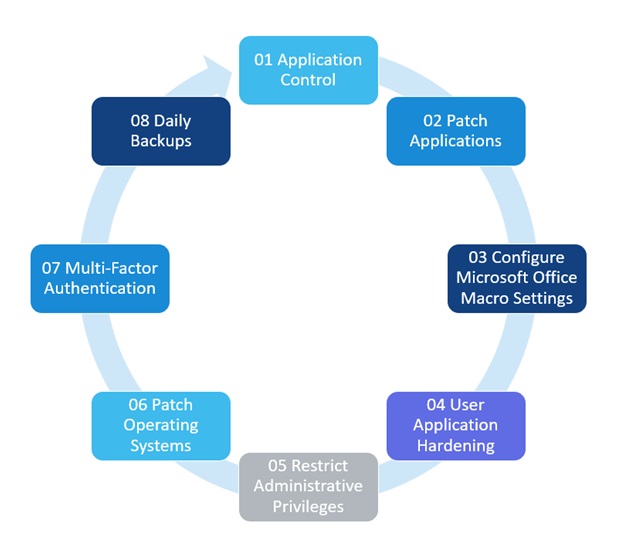
1. Application whitelisting
Application whitelisting, otherwise known as application control, is a tactic that entails limiting the use of unauthorized software on a company’s systems. This is the application control to defend against malicious code, including DLLs and executable files like.exe.
This control is vital to add the additional layer of security required for commercial systems because antivirus software can’t find every unauthorized program. It makes it harder for malware and other harmful applications to operate on the systems. As mentioned earlier, each of these strategies must follow the 4 levels of maturity as follows:
- Level 0: As of right now, the organization hasn’t put any application whitelisting controls in place.
- Level 1: At this stage, the organization currently has a plan in place to adopt application whitelisting controls.
- Level 2: Here, the application whitelisting mechanisms have been put in place at this point, and the company is keeping an eye on them.
- Level 3: At this level, the business currently has a mechanism in place for maintaining application whitelisting measures, and it is continually enhancing these measures.
2. The Application Patching
Just as the word suggests, to patch is to strengthen the operating system. The practice of patching operating systems and apps includes keeping them up to date with the most recent security updates.
This aids in the prevention of cyberattacks that make use of software weaknesses.
3. Restricting Administrative Privileges
There are accounts with privileges above those of regular users in almost every environment. This allows them to add, remove, and modify information system components. These accounts, which include dedicated service accounts for automatic execution, offer a great deal of power and have the potential to bring about many tragedies if utilized improperly.
However, administrative privileges can be local, domain, or enterprise level and have varying degrees of control. Some people may only consider the administrator accounts used directly on servers or in Active Directory. Beyond that, they are present on desktops, networking devices, and pretty much every other IoT-related hardware.
This strategy involves limiting the number of users with administrative rights on a system within a company. By doing this, assaults that abuse administrative privileges are deterred.
The four stages of maturity for this strategy are broken down by the Essential Eight model as follows:
- Level 1: At this initial stage, the organization hasn’t yet put any restrictions on administrative privileges into place.
- Level 2: When a vulnerability is found or an attack takes place, the organization restricts administrative privileges at this point.
- Level 3: Proactive: At this stage, the company is aggressively limiting administrative rights to thwart attacks before they happen.
- Level 4: The business currently has a written procedure in place for managing administrator rights and is working to continually improve these controls.
4. Patching Operating Systems
Similar to the patching of applications, the OS also needs to be patched. This involves updating operating systems with the most recent security updates
The operating system is the brain of the computer and is necessary for the operation of all other components. It functions on a wide range of platforms, including Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix, mobile devices, network devices, and the Internet of Things. Apps would be useless without them, much like a car without an engine would be.
Operating systems require critical maintenance upgrades to keep everything running smoothly. This aids in preventing attacks that take advantage of well-known operating system flaws.
5. Configuring the Microsoft Office macro settings
Macros are a batch of commands and processes grouped to make life easier. They can, however, also be misused, which produced the Melissa and Wazzu macro viruses. Microsoft has made significant efforts to safeguard macros in Office, but these efforts are insufficient to shield users from themselves.
To stop harmful macros from running in Microsoft Office programs, one tactic is to configure the macro settings in Microsoft Office. This aids in thwarting assaults that disseminate malware via macros.
6. Using Application Hardening
Installing applications with defaults can make them more secure and less likely to be used against us. To reduce the likelihood of a successful cyberattack, limiting user access to specific programs and services is very essential. By doing this, attacks that abuse user privileges are deterred.
Regularly reviewing who can access an application and what it can do is a good approach.
7. Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security measure that requires users to provide another means of identifying themselves, such as a username and password. It is supplemented by mobile apps, SMS codes, and smart cards. Biometric authentication is also being used, such as fingerprint scanners and touch IDs on mobile devices. Given the current threat landscape, it is becoming a must for cloud-centric strategies.
8. Regular/ Daily Backups
Last but not least, data backup has been a tried-and-true method for keeping your information safe when things go wrong.
Backing up data is essential to ensure it can be recovered in the event of a disaster, such as a Ransomware attack. There are many options at different price points, including magnetic and optical media, cloud-based storage, and Disaster Recovery Sites. Restoring data without it being incomplete, corrupted, or inaccessible is essential.
Before you start executing the above strategies, make sure to:
- Perform risk analysis: Risk assessment helps organizations prioritize cybersecurity efforts and identify the most important strategies.
- Create a security strategy: You should develop a comprehensive security plan to address identified risks and vulnerabilities.
Now you can start implementing the strategies one after the other. After taking care of the above, you must now systematically implement the strategies.
Next, start to monitor and evaluate the performance. This will make it easier to spot any areas in need of development and guarantee that the company’s cybersecurity defenses are always changing to counter new threats.
Conclusion
Organizations must take a proactive approach to cybersecurity even as the threat landscape changes constantly. A useful and effective road map for accomplishing this aim is provided by The Essential 8. Remember that cybersecurity is an ongoing process, and implementing the ACSC Essential Eight Framework is just the beginning. Continuously monitor your systems, stay informed about emerging threats, and regularly review and update your security measures to address new vulnerabilities.
Table of contents
Related Posts
We’ll handle the tech
so you can get on with
running your business.

CALL US
1300 414 214
Our Trusted Partners
Contact Us
Let’s Talk
Common Questions
Do you outsource your work overseas?
No. We use local teams only. That way we can respond more quickly to any problems that may occur. We want your tech running smoothly so you can focus on what you do best.
Is your support 24 hours?
Yes. We have people available whenever you need us. We understand that your tech runs 24 hours, and you need it be working at all times.
Are your services customised for my business?
Yes. There is great off the shelf software. But we know one size never fits all. So anything we set up for you is designed to make your business run smoother and in the way you want it to.
Are your services expensive?
No. Reliable tech is the life blood of your business. We keep it running smoothly so your business can keep making money. All our services are fixed fees, so you never get any nasty surprises.
What’s the next step?
Simply book a chat with one of our experts. We’ll have a chat about exactly what you need and how we can help. If you like our approach then we’ll give you a fixed price quote and get everything up and running for you, fast!